AFTER OVERHAULING an AUXILIARY ENGINE various measurement and inspection of all parts of engine is done. The DETAILS are given below;
1.Inspection of Valves/Valve Seats
-If the valve seat is burnt or scarred, it should be ground using a valve seat grinder, please see working card
505-01.10.
2.Inspection of Valve Guide
Too much clearance between the valve spindle and the spindle guide may cause:
- increased lub. oil consumption.
- fouling up of the spindle guide and thus give the risk of the sticking of the valve spindle.
1) Clean the valve spindle guide.
2) Inspect and measure for wear.
If the inner diameter of the valve spindle guide exceeds the tolerance, please see page 500.35,the valve spindle guide must be replaced.Please see working card 505-01.20.
Too much clearance also means insufficient guidance of the valve spindle, and thus bad alignment between the spindle head and the valve seat ring.
3.Maintenance and Inspection of Rotocap
Dirt, especially in the ball pockets due to residues in the oil (abrasives, combustion products), can cause the individual parts to become stuck, and interrupt the movement of the balls.Under normal operating conditions rotocap valve rotators need no servicing.
Rotator performance is satisfactory when the valve rotates visibly and evenly.
3.Inspection of Cylinder Head Cooling Water Space
1) Inspect the cooling water inlet at the bottom of the cylinder head, see fig 1.
2) Remove all possible deposits.
3) If necessary, clean the cooling water inlet and cooling water outlet, see fig 1 with a steel brush.Flush the cooling water space after cleaning.
4) Should the cylinder head cooling water space, contrary to expectation, be blocked with deposits, please contact MAN B&W Diesel.
4.Inspection of Piston
1) Remove the piston and scraper rings.
2) Clean the piston on the outside and on the inside.
3) Inspect the piston ring and scraper ring grooves for wear.
4) condition of carbon deposits on the piston and lubricating condition , scratch and abnormal contact of sliding areas, condition of carbon sludge deposit on the Piston underside ,abnormal contact of the Piston pin and pin Bush inner surface.
Check of Piston Bolt Tension
4) Apply a torque spanner to the piston bolts, adjusted to 20 Nm.
5) Turn the torque spanner.
Maintenance- clean all parts, blow air to oil hole and clean inside of the hole, perform inspection for crack by means of colour check.
Measurement -
1)Piston outer diameter using an external micrometre at four places .
2)clearance between cylinder liner inner diameter and Piston outer diameter 3)Piston pin outer diameter and Piston pin Bush inner diameter.
5.Inspection of Piston Crown
For cleaning and inspection of the piston crown, it must be disassembled.
6) Loosen the bolts and remove the piston
crown.
7)check for cracks by dye penerant test.
7) Clean carefully the piston shirt and piston.The piston crown must be scrapped if:
A) The wear limit on the testing mandrel is exceeded, see fig 1A
or
B) The clearance between the new piston/scraper
ring and the ring groove is exceeded, see fig 1B.
Note: At each piston overhaul:
- The piston and the scraper ring must be
replaced.
- The cylinder liner must be honed according to the instructions.
- For position and fittings of piston rings,
please see working card.
6.Cleaning of Connecting Rod
1) Clean all machined surfaces on the connecting rod.
2) Degrease the joint faces, holes and connecting rod screws with a volatile solvent and blow dry with working air.
Visual Inspection of Faces
3) Inspect the joint faces.Damages, in the form of visible wear marks and pittings or even cracks, may be in the joint faces due to relative movements between the surfaces.
Wear marks and cracks are visible, but not
perceptible with a fingernail. Pittings and impact marks are both visible and perceptible. Dent or peel of the threaded areas and seat surfaces of the connecting rod joint Bolt. Check by dye penetrant
5) Carefully smooth single raised spots in the serration caused by pitting and impact marks with a file.
7.Inspection of Connecting Rod bolts
6) Inspect the connecting rod nuts for seizures in the threads and pittings on the contact surfaces of the screwheads.
7) Turn the connecting rod nuts onto bottom position of the bolts.
Measurement of Big-end Bore
For check of ovalness the bearing cap has to be mounted onto the big-end bore without bearing shells.Fig 1 Point of measurement
8) Mount the bearing cap onto the connecting rod by means of the connecting rod bolts.
9) Tighten the bolts with the prescribed pressure, please see working card .
10) Measure five different diameters in the groove of the boring.
11) Register the measurements.
12) Calculate the maximum ovalness as the difference between biggest and smallest diameter measured.
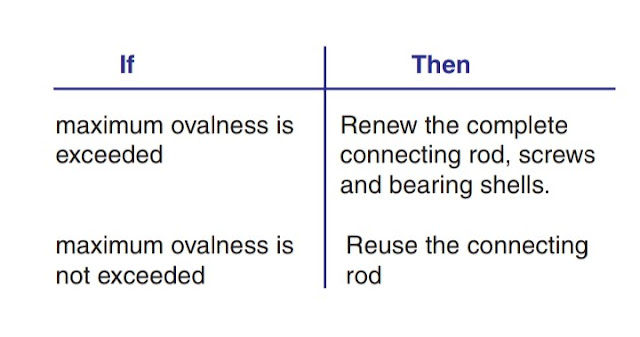
13) Check if maximum ovalness is exceeded
Example of Measurement Results
(in case the specified maximum ovalness is exceeded, contact MAN Diesel for overhaul).
For connecting rod No 1 in the example the maximum ovalness is 0.02 mm and thus reuse is acceptable.
For connecting rod No 2 in the example the maximum ovalness is 0.125 mm and therefore the connecting rod is rejected.
Connecting rod bolt rejection criteria
-Loading of connecting rod bolts of 4 stroke is more severe than two stroke engine as RPM difference 100 and 1200 RPM.
- the centrifugal force and gas force Set up bending and shear stresses in the bolts ,as a result fatigue failure occurs in bolts.
-bolts should be constructed of material having high resilience and should not be stiffer with respect to bearing housing .
Subroutine checks on this part are the (rejection criteria of the bolts )
-check the corrosion by acidic Lube oil discard if any present on shanks.
- check the length of the Bolt against a new or Bolt tolerance it longer yielding of the material should have taken place renew the Bolt in this circumstance.
- check for mechanical damage especially on shanks .
-check for fracture by non destructive test --
-check the landing phases for an uneven tightening .
-discard the Bolt when either designated life, over speed failure or piston seizure has occurred.
8.Inspection of Connecting Rod Bush
14) Inspect the surface of the piston pin and the connecting rod bush.
15) Measure the clearance between the piston pin and bush.
16) Check if max clearance is exceeded
If the specifi ed clearance is exceeded, con tact MAN Diesel for replacement.
9.Inspection of main bearing shell for big end bearing
1)check for Cavitation erosion.
2) scratches due to foreign material .
3)scoring deep replace wearing .
4)Fatigue rupture.
5) check for tin oxide corrosion due to water in Lube oil, tin oxide is formed which is hard and brittle with high load this layer can break at high bearing temperature and melt it and failure of a by wiping.
6) wiping of bearing surfaces due to lack of oil -too small bearing clearance.
10.Inspection and maintenance of crank pin shell.
-inspect if there is not fretting on the crank pin shell, also for seizure mark, Cavitation or any embedded foreign matters. repair using oil stone.
- measure shell thickness using spherical micrometer.
- calculate clearance from measurement of inner diameter of large housing thickness of Shell and diameter of crankpin.
-oxidation leads to black is colour .Dye penetrant test and colour check for cracking and scoring.
11.Inspection and maintenance of liners.
-Remove scale or silicone rubber accumulated on the liner outer Periphery using a wire brush.
- Colour check and crack check. Inspect liner outer Periphery for Cavitation or corrosion or freeting. Reason for corrosion or Cavitation 1)cooling water rust preventive agent is not working properly 2)cooling water pressure is low 3) cooling water is mixed with air.
-measure the inner dia of liner in port-stbd and fwd-aft by internal micrometer. Compare with previous reading to get wear down of liner.
Measurement of Cylinder Diameter
While the piston is removed from the cylinder, the latter is measured to record the wear. The measurements are taken by means of an inside micrometer,
with measuring points at TDC-position for the upper-most piston ring, halfway down, and at the BDC in the cylinder liner.
The measurements normally should be taken in both transverse and in longitudinal direction.When measuring, take care that the measuring tool has approximately the same temperature as the liner.
When the wear of a cylinder liner exceeds the value indicated on , when it becomes too troublesome to maintain adequate service conditions, the cylinder liner in question should be replaced.
So overall measurement in auxiliary engine are as follows:
1.piston pin outer dia and piston bush inner dia.
2. The axial clearance of piston ring-0.40mm max.
3. Liner wear rate by measuring inner dia of liner
4. ovalness of bearing cap without bearing shell .
5. Diameter of crankpin .
6. Piston outside dia and liner inside dia.
1.Inspection of Valves/Valve Seats
-If the valve seat is burnt or scarred, it should be ground using a valve seat grinder, please see working card
505-01.10.
2.Inspection of Valve Guide
Too much clearance between the valve spindle and the spindle guide may cause:
- increased lub. oil consumption.
- fouling up of the spindle guide and thus give the risk of the sticking of the valve spindle.
1) Clean the valve spindle guide.
2) Inspect and measure for wear.
If the inner diameter of the valve spindle guide exceeds the tolerance, please see page 500.35,the valve spindle guide must be replaced.Please see working card 505-01.20.
Too much clearance also means insufficient guidance of the valve spindle, and thus bad alignment between the spindle head and the valve seat ring.
3.Maintenance and Inspection of Rotocap
Dirt, especially in the ball pockets due to residues in the oil (abrasives, combustion products), can cause the individual parts to become stuck, and interrupt the movement of the balls.Under normal operating conditions rotocap valve rotators need no servicing.
Rotator performance is satisfactory when the valve rotates visibly and evenly.
3.Inspection of Cylinder Head Cooling Water Space
1) Inspect the cooling water inlet at the bottom of the cylinder head, see fig 1.
2) Remove all possible deposits.
3) If necessary, clean the cooling water inlet and cooling water outlet, see fig 1 with a steel brush.Flush the cooling water space after cleaning.
4) Should the cylinder head cooling water space, contrary to expectation, be blocked with deposits, please contact MAN B&W Diesel.
4.Inspection of Piston
1) Remove the piston and scraper rings.
2) Clean the piston on the outside and on the inside.
3) Inspect the piston ring and scraper ring grooves for wear.
4) condition of carbon deposits on the piston and lubricating condition , scratch and abnormal contact of sliding areas, condition of carbon sludge deposit on the Piston underside ,abnormal contact of the Piston pin and pin Bush inner surface.
Check of Piston Bolt Tension
4) Apply a torque spanner to the piston bolts, adjusted to 20 Nm.
5) Turn the torque spanner.
Maintenance- clean all parts, blow air to oil hole and clean inside of the hole, perform inspection for crack by means of colour check.
Measurement -
1)Piston outer diameter using an external micrometre at four places .
2)clearance between cylinder liner inner diameter and Piston outer diameter 3)Piston pin outer diameter and Piston pin Bush inner diameter.
5.Inspection of Piston Crown
For cleaning and inspection of the piston crown, it must be disassembled.
6) Loosen the bolts and remove the piston
crown.
7)check for cracks by dye penerant test.
7) Clean carefully the piston shirt and piston.The piston crown must be scrapped if:
A) The wear limit on the testing mandrel is exceeded, see fig 1A
or
B) The clearance between the new piston/scraper
ring and the ring groove is exceeded, see fig 1B.
Note: At each piston overhaul:
- The piston and the scraper ring must be
replaced.
- The cylinder liner must be honed according to the instructions.
- For position and fittings of piston rings,
please see working card.
6.Cleaning of Connecting Rod
1) Clean all machined surfaces on the connecting rod.
2) Degrease the joint faces, holes and connecting rod screws with a volatile solvent and blow dry with working air.
Visual Inspection of Faces
3) Inspect the joint faces.Damages, in the form of visible wear marks and pittings or even cracks, may be in the joint faces due to relative movements between the surfaces.
Wear marks and cracks are visible, but not
perceptible with a fingernail. Pittings and impact marks are both visible and perceptible. Dent or peel of the threaded areas and seat surfaces of the connecting rod joint Bolt. Check by dye penetrant
5) Carefully smooth single raised spots in the serration caused by pitting and impact marks with a file.
7.Inspection of Connecting Rod bolts
6) Inspect the connecting rod nuts for seizures in the threads and pittings on the contact surfaces of the screwheads.
7) Turn the connecting rod nuts onto bottom position of the bolts.
Measurement of Big-end Bore
For check of ovalness the bearing cap has to be mounted onto the big-end bore without bearing shells.Fig 1 Point of measurement
8) Mount the bearing cap onto the connecting rod by means of the connecting rod bolts.
9) Tighten the bolts with the prescribed pressure, please see working card .
10) Measure five different diameters in the groove of the boring.
11) Register the measurements.
12) Calculate the maximum ovalness as the difference between biggest and smallest diameter measured.
13) Check if maximum ovalness is exceeded
Example of Measurement Results
(in case the specified maximum ovalness is exceeded, contact MAN Diesel for overhaul).
For connecting rod No 1 in the example the maximum ovalness is 0.02 mm and thus reuse is acceptable.
For connecting rod No 2 in the example the maximum ovalness is 0.125 mm and therefore the connecting rod is rejected.
Connecting rod bolt rejection criteria
-Loading of connecting rod bolts of 4 stroke is more severe than two stroke engine as RPM difference 100 and 1200 RPM.
- the centrifugal force and gas force Set up bending and shear stresses in the bolts ,as a result fatigue failure occurs in bolts.
-bolts should be constructed of material having high resilience and should not be stiffer with respect to bearing housing .
Subroutine checks on this part are the (rejection criteria of the bolts )
-check the corrosion by acidic Lube oil discard if any present on shanks.
- check the length of the Bolt against a new or Bolt tolerance it longer yielding of the material should have taken place renew the Bolt in this circumstance.
- check for mechanical damage especially on shanks .
-check for fracture by non destructive test --
-check the landing phases for an uneven tightening .
-discard the Bolt when either designated life, over speed failure or piston seizure has occurred.
8.Inspection of Connecting Rod Bush
14) Inspect the surface of the piston pin and the connecting rod bush.
15) Measure the clearance between the piston pin and bush.
16) Check if max clearance is exceeded
If the specifi ed clearance is exceeded, con tact MAN Diesel for replacement.
9.Inspection of main bearing shell for big end bearing
1)check for Cavitation erosion.
2) scratches due to foreign material .
3)scoring deep replace wearing .
4)Fatigue rupture.
5) check for tin oxide corrosion due to water in Lube oil, tin oxide is formed which is hard and brittle with high load this layer can break at high bearing temperature and melt it and failure of a by wiping.
6) wiping of bearing surfaces due to lack of oil -too small bearing clearance.
10.Inspection and maintenance of crank pin shell.
-inspect if there is not fretting on the crank pin shell, also for seizure mark, Cavitation or any embedded foreign matters. repair using oil stone.
- measure shell thickness using spherical micrometer.
- calculate clearance from measurement of inner diameter of large housing thickness of Shell and diameter of crankpin.
-oxidation leads to black is colour .Dye penetrant test and colour check for cracking and scoring.
11.Inspection and maintenance of liners.
-Remove scale or silicone rubber accumulated on the liner outer Periphery using a wire brush.
- Colour check and crack check. Inspect liner outer Periphery for Cavitation or corrosion or freeting. Reason for corrosion or Cavitation 1)cooling water rust preventive agent is not working properly 2)cooling water pressure is low 3) cooling water is mixed with air.
-measure the inner dia of liner in port-stbd and fwd-aft by internal micrometer. Compare with previous reading to get wear down of liner.
Measurement of Cylinder Diameter
While the piston is removed from the cylinder, the latter is measured to record the wear. The measurements are taken by means of an inside micrometer,
with measuring points at TDC-position for the upper-most piston ring, halfway down, and at the BDC in the cylinder liner.
The measurements normally should be taken in both transverse and in longitudinal direction.When measuring, take care that the measuring tool has approximately the same temperature as the liner.
When the wear of a cylinder liner exceeds the value indicated on , when it becomes too troublesome to maintain adequate service conditions, the cylinder liner in question should be replaced.
So overall measurement in auxiliary engine are as follows:
1.piston pin outer dia and piston bush inner dia.
2. The axial clearance of piston ring-0.40mm max.
3. Liner wear rate by measuring inner dia of liner
4. ovalness of bearing cap without bearing shell .
5. Diameter of crankpin .
6. Piston outside dia and liner inside dia.




























No comments:
Post a Comment